Java programming language provides platform independence, what does it mean ? It means same java program can be run on any platform or operating system e.g. Windows, Linux or Solaris without any change. This is the great benefit for some one coming from platform dependent programming language like C or C++ whose code needs to be ported for every single platform because they use native libraries which differ in every platform. Now question comes how Java achieve platform independence, what makes Java programs running on every platform without any change ? This is one of the most basis question java programmer ask when it start learning java programming language. if you read further you will come to know about byte code and Java virtual machine which together provides platform independence to Java.
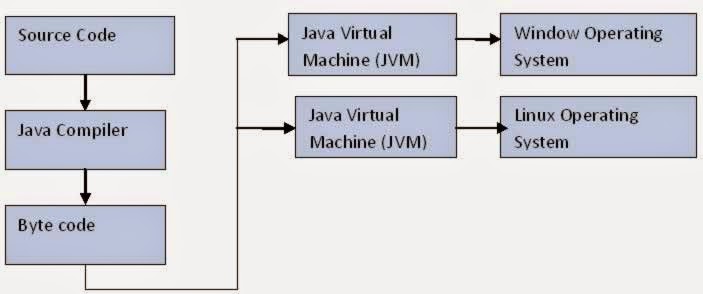
For those who don't know Java is both compiler and interpreter language. When you compile a Java program it creates .class file which is collection of byte code, these byte code are not machine instruction instead they are instruction which Java virtual machine can understand. Since every Java program runs on Java virtual machine, same byte code can be run on any platform. key is byte code is not machine instruction they are platform independent instruction to JVM. On the other hand JVM or Java virtual machine is platform dependent because it converts byte code into machine level instruction which is platform specific and that's why you have different version of JDK and JRE for windows and Linux because both JDK and JRE comes with Java virtual machine. if you are confused between JVM, JRE and JDK then read my most on difference between JDK, JRE and JVM in java.
Byte code is created when you compile Java program using java compiler "javac" and byte code runs on JVM which is created by running "java" command. In detail when you run "java" command it creates Java virtual machine, loads Main class specified in command line and calls standard main method in java.
In summary combination of byte code and JVM makes Java program platform independent. Write once run everywhere was Java’s mantra when it started ruling programming world in mid and late 90’s.
For those who don't know Java is both compiler and interpreter language. When you compile a Java program it creates .class file which is collection of byte code, these byte code are not machine instruction instead they are instruction which Java virtual machine can understand. Since every Java program runs on Java virtual machine, same byte code can be run on any platform. key is byte code is not machine instruction they are platform independent instruction to JVM. On the other hand JVM or Java virtual machine is platform dependent because it converts byte code into machine level instruction which is platform specific and that's why you have different version of JDK and JRE for windows and Linux because both JDK and JRE comes with Java virtual machine. if you are confused between JVM, JRE and JDK then read my most on difference between JDK, JRE and JVM in java.
Byte code is created when you compile Java program using java compiler "javac" and byte code runs on JVM which is created by running "java" command. In detail when you run "java" command it creates Java virtual machine, loads Main class specified in command line and calls standard main method in java.
In summary combination of byte code and JVM makes Java program platform independent. Write once run everywhere was Java’s mantra when it started ruling programming world in mid and late 90’s.
Comments
Post a Comment